AWS Lambda Functions — Serverless Architecture, Use Cases & Cost Guide (2025)
By Mahipalsinh Rana November 6, 2023
Why AWS Lambda Matters for Modern Enterprises
Enterprises are moving away from always-on servers toward event-driven, scalable, and cost-efficient architectures. AWS Lambda plays a key role by enabling teams to focus on business logic instead of infrastructure management.
AWS Lambda helps enterprises:
- Eliminate server provisioning & patching
- Scale instantly for unpredictable workloads
- Reduce infrastructure cost significantly
- Build highly decoupled, event-driven systems
- Accelerate time-to-market
Lambda is widely used in FinTech, SaaS, logistics, healthcare, eCommerce, and government platforms.
What Is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) offering from AWS that lets you run code in response to events — without provisioning or managing servers.
Key characteristics:
- Stateless execution
- Automatic scaling
- Millisecond-level billing
- Event-driven invocation
- Deep integration with AWS services
Lambda functions are triggered by events such as:
- HTTP requests (API Gateway)
- File uploads (S3)
- Database changes (DynamoDB Streams)
- Messages (SQS / SNS)
- Scheduled jobs (EventBridge)
Common Enterprise Use Cases for AWS Lambda
- Backend APIs for web & mobile apps
- Event-driven data processing
- Real-time file & image processing
- Payment & transaction workflows
- ETL & data transformation jobs
- Automation & cron replacements
- Microservices & integration layers
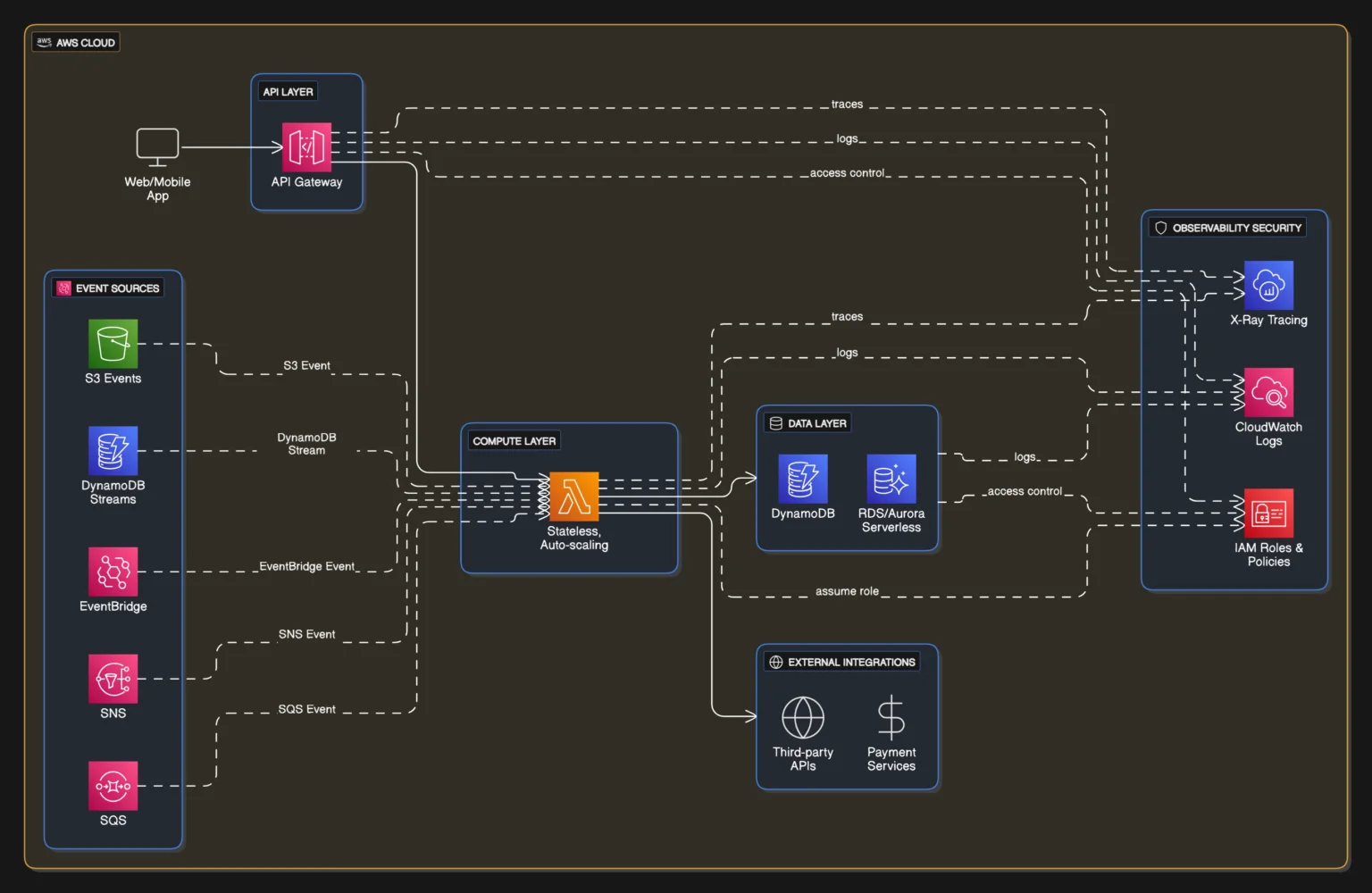
AWS Lambda Architecture Overview
In an enterprise serverless architecture, AWS Lambda typically sits at the center of an event-driven system.
Core architectural components include:
- Client Applications (Web / Mobile)
- API Gateway (request routing & auth)
- AWS Lambda functions (business logic)
- Event sources (S3, SQS, SNS, EventBridge)
- Data stores (DynamoDB, Aurora Serverless)
- Security (IAM roles & policies)
- Observability (CloudWatch, X-Ray)
AWS Lambda Languages & Runtime Support
AWS Lambda supports multiple runtimes:
- Java
- Python
- Node.js
- .NET
- Go
- Ruby
Enterprises typically choose:
- Java / .NET for complex enterprise logic
- Python for data processing & automation
- Node.js for APIs & lightweight microservices
AWS Lambda Pricing & Cost Considerations
| Cost Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Execution Time | Charged per millisecond |
| Memory Size | Higher memory = higher CPU |
| Requests | Charged per invocation |
| Data Transfer | Standard AWS networking charges |
Indicative Monthly Cost
- Small workloads: $5 – $20
- Medium enterprise systems: $50 – $300
- High-scale event systems: $500+
Why Enterprises Save Cost
- No idle server cost
- Pay only for execution
Automatic scaling eliminates over-provisioning
AWS Lambda Limitations (Enterprise Perspective)
- Execution timeout (max 15 minutes)
- Cold start latency (important for APIs)
- Not ideal for long-running jobs
- Limited local disk space
- Complex debugging vs traditional servers
Avoid Lambda For
- Heavy CPU-bound workloads
- Long-running batch jobs
- Low-latency, always-warm systems
Best Practices for Production-Grade AWS Lambda
- Keep functions small & single-purpose
- Use environment variables for config
- Apply least-privilege IAM policies
- Enable structured logging
- Use retries & DLQs for failure handling
- Monitor with CloudWatch & X-Ray
- Combine Lambda with Step Functions for workflows










