Building Microservices in Python — Architecture, Tools & Best Practices (2025 Guide)
By Dharmesh Patel January 13, 2023
Why Enterprises Choose Microservices Architecture
Monolithic applications become difficult to scale, deploy, and maintain as systems grow.
Microservices solve this by splitting applications into small, independent services, each focused on a single business capability.
Key enterprise benefits:
- Independent scaling & deployment
- Faster release cycles
- Fault isolation
- Technology flexibility
- Better team autonomy
Python’s simplicity and ecosystem make it a strong choice for microservices-based systems.
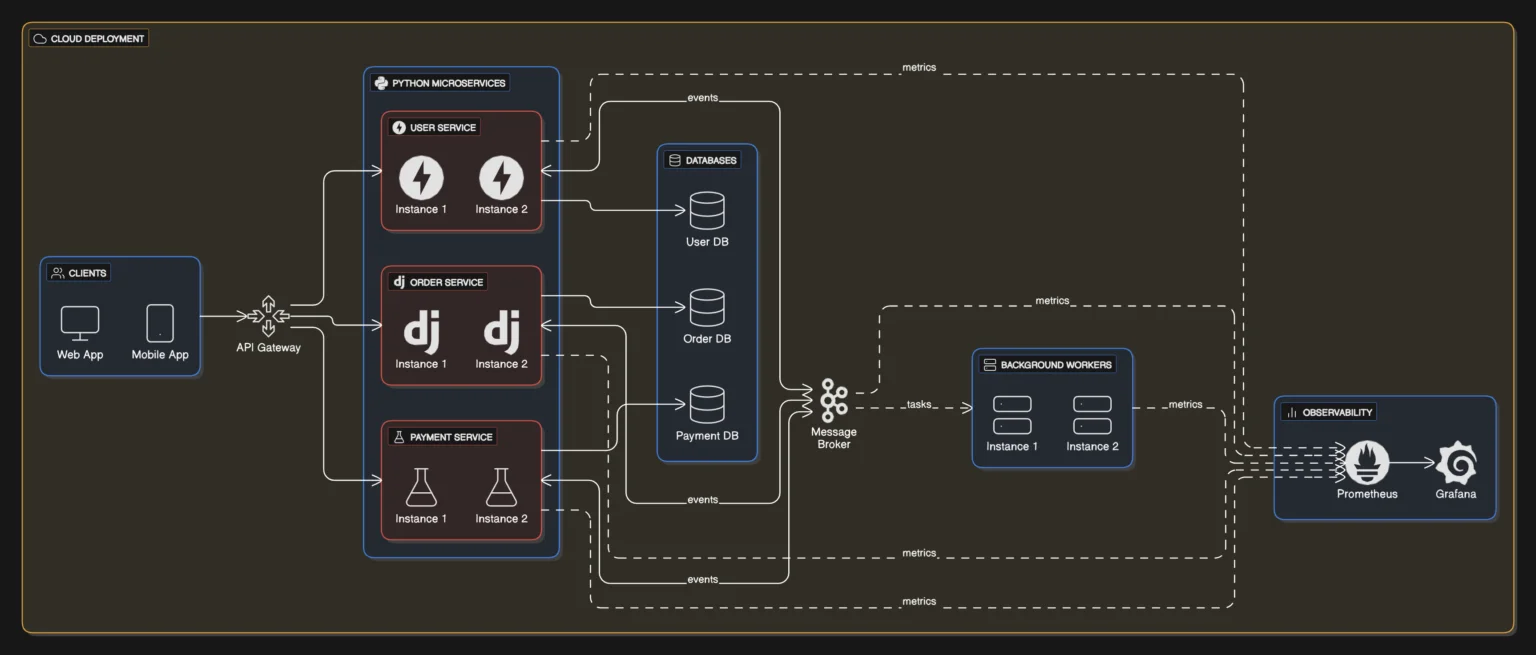
Python Microservices Architecture Overview
A typical Python microservices architecture includes:
- Client Applications
Web apps, mobile apps, or external systems. - API Gateway
Single entry point handling routing, auth, rate-limiting, and logging. - Python Microservices
Independent services built with FastAPI, Django, or Flask. - Databases per Service
Each service owns its data to avoid tight coupling. - Async Messaging Layer
Kafka / RabbitMQ for event-driven workflows. - Observability Layer
Centralized logging, metrics, and tracing.
Python Frameworks for Microservices
Popular choices include:
FastAPI
- Async-first
- High performance
- OpenAPI support
- Ideal for modern APIs
Django + DRF
- Mature ecosystem
- Built-in admin
- Suitable for complex business logic
Flask
- Lightweight
- Flexible
- Good for small services
Enterprise Recommendation:
FastAPI for performance-critical services, Django for business-heavy domains.
Communication Between Microservices
Microservices communicate using two primary patterns:
Synchronous (REST / gRPC)
- Simple request-response
- Used for real-time operations
Asynchronous (Events / Messaging)
- Kafka, RabbitMQ
- Loose coupling
- High scalability
Enterprise Best Practice:
Use async events for workflows, REST only where immediate responses are required.
Database per Microservice Pattern
Each microservice must own its database.
Benefits:
- Prevents tight coupling
- Independent schema evolution
- Service autonomy
Common stacks:
- PostgreSQL / MySQL (transactional)
- MongoDB (document-based)
- Redis (caching)
- Elasticsearch (search)
Avoid shared databases across services.
Deploying Python Microservices at Scale
Enterprise deployment typically uses:
- Docker containers
- Kubernetes orchestration
- Auto-scaling policies
- Blue-green or rolling deployments
Python microservices scale horizontally by running multiple stateless instances behind load balancers.
Securing Python Microservices
- API Gateway authentication (JWT / OAuth2)
- mTLS between services
- Secrets management (Vault / AWS Secrets Manager)
- Rate limiting
- Input validation
- Secure inter-service communication
Security must be designed into the architecture, not added later.
Monitoring & Debugging Microservices
Enterprise systems require full observability:
- Centralized logging
- Distributed tracing
- Metrics & alerts
Popular tools:
- Prometheus & Grafana
- ELK Stack
- OpenTelemetry
- Jaeger
Without observability, microservices become unmanageable at scale.
Best Practices for Python Microservices
- Keep services small & focused
- Avoid shared databases
- Prefer async communication
- Implement retries & circuit breakers
- Version APIs properly
- Automate CI/CD pipelines
- Enforce coding standards
- Design for failure









