AI Development for Enterprises: Cost,...
July 3, 2025

Digital commerce, commonly known as e-commerce, has altered the way we buy and sell goods online.
In this article, we’ll take a look at what digital commerce is, what its parts are, and what it means to influence online buying. Whether you manage a business and wish to sell online, appreciate purchasing online, or are basically inquisitive about how innovation has changed buying, this book gives significant data to you. We’ll investigate the exciting world of online buying and selling and separate it for you. Let’s get started and learn about the many methods we may shop and sell online!
Digital commerce is all about buying and selling goods and services through the Internet and other digital means. This includes not just making online purchases but also involves things like electronic payments and using digital strategies for marketing.
This sort of commerce is a part of eCommerce, which you could have seen with online stores. These stores are intended to be easy to understand, offering things like simple methods for finding what you’re searching for, detailed descriptions of products, reviews, audits from different clients, and safe ways of paying. A few notable instances of these online business stages are Amazon, eBay, Etsy, and Shopify.
As indicated by late information from Statista, digital commerce is a gigantic piece of the global market. It’s assessed to be worth around $4.9 trillion and around 24.5% of all retail sales around the world.
Taking a gander at it according to the client’s perspective, digital commerce allows individuals to collaborate with brands and purchase things utilizing their digital devices all alone. For businesses, it includes much more. They need the right innovation to deal with online sales and marketing, explicit jobs in the company zeroed in on online commerce, content to draw in and keep online clients, procedures to get new clients and make them want more, and various ways of setting costs online.
The development of digital commerce can be ascribed to a few key factors that have changed the manner in which businesses work and how customers shop. Here are a portion of the significant purposes behind its development.
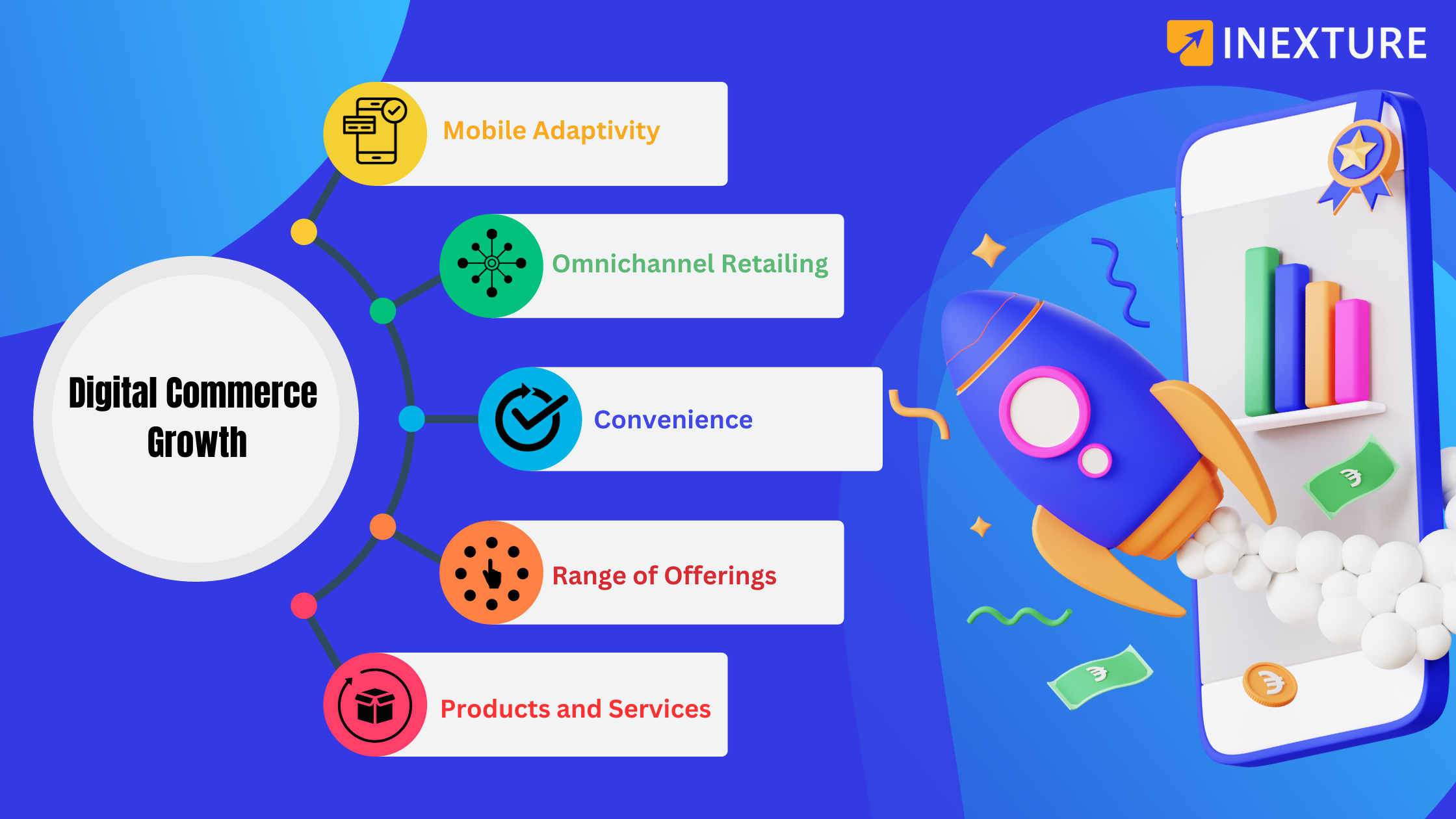
Mobile Adaptivity: With the far-reaching utilization of smartphones, digital commerce has adapted to be more mobile-friendly. Individuals presently can shop from any place, whenever, utilizing their mobile devices. This straightforward entry has added to the development of the growth of online shopping.
Omnichannel Retailing: This approach coordinates different techniques for shopping accessible to customers, for example, shopping online from a desktop or mobile device, by telephone, or in a brick-and-mortar store. Omnichannel retailing makes a consistent shopping experience for the client, regardless of how they decide to shop.
Convenience: Digital commerce offers unparalleled convenience. Clients can shop all day, every day, stay away from the issue of traveling to a store, and easily compare prices and products from different vendors. This convenience factor is a significant driving force behind the growth of online shopping.
Greater Range of Offerings: Online platforms can offer a lot more extensive scope of items than traditional stores, because of the absence of physical space limits. This variety attracts a broader range of customers and meets diverse needs and preferences, thereby boosting sales in digital commerce.
Individualized Products and Services: Digital commerce platforms can fit their contributions and marketing to individual customers, in light of their perusing and buying history. This personalization upgrades the shopping experience and can prompt expanded consumer loyalty and reliability.
Recommend Read: How Much Time Does It Take to Build an E-commerce App?
Digital commerce contains many exercises and components that together make the total online shopping and selling experience. At its center, it incorporates the buying and selling of goods and services through digital platforms, primarily the Internet.
This process involves something other than the exchange of buying things online; it additionally incorporates pre-sale and post-sale activities. Pre-sale activities involve marketing strategies, customer engagement through social media and email campaigns, and providing detailed product information on websites.
Post-sale activities include customer support, managing returns and exchanges, and gathering feedback for future improvements.
In addition to these aspects, digital commerce also involves the technological infrastructure that makes online transactions possible.
This includes secure payment gateways, inventory management systems, and sophisticated algorithms for personalized recommendations. E-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify are prime examples, offering user-friendly interfaces, easy navigation, and a range of payment options to facilitate smooth transactions.
Besides, digital commerce isn’t confined to business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions yet in addition incorporates business-to-business (B2B) models, where companies execute with one another utilizing digital platforms. The flexibility and far-reaching nature of digital commerce make it an essential part of the advanced global economy.
Digital commerce is important for several compelling reasons, shaping not only the business world but also consumer behavior and the global economy.
First and foremost, it gives accessibility and convenience, which are maybe the main advantages. Clients can shop from any place whenever, without the impediments of store hours or geological boundaries. This comfort has prompted a significant expansion in online shopping, making it an essential piece of the retail area.
Secondly, digital commerce offers businesses a wider reach. It permits even small businesses to get to worldwide business sectors, breaking down the barriers that traditional brick-and-mortar stores face. This extended reach likewise encourages rivalry, prompting better quality items and administrations at competitive costs for purchasers.
Thirdly, it empowers personalization and further develops client encounters. Online stages can follow client inclinations and shopping ways of behaving, permitting organizations to fit their contributions and promoting techniques to individual clients. This degree of personalization improves consumer loyalty and dependability.
Fourthly, digital commerce is cost-effective for businesses. It reduces the need for physical stores, cutting down on overhead costs like rent, utilities, and in-store staff. Additionally, digital marketing strategies can be more targeted and efficient compared to traditional marketing, offering a better return on investment.
Lastly, digital commerce drives innovation and growth. The need to stay competitive in the online marketplace pushes businesses to ceaselessly improve as far as their product contributions, customer service, and technological advancements. This innovation not only benefits consumers but also propels the industry forward, contributing to economic growth.
The importance of digital commerce lies in its ability to offer convenience and accessibility to consumers, expanded market reach and cost-effectiveness for businesses, personalized shopping experiences, and its role in driving innovation and economic growth.
Digital commerce is utilized in various ways, both by businesses and consumers, to work with and improve the buying and selling process online. This is the way it’s generally utilized:

Online Retail Stores: The most apparent utilization of digital commerce is through online retail platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify. Here, businesses list items or services for sale, and consumers can browse, select, select, and buy these things from the solace of on-the-go using mobile devices.
Mobile Commerce: With the rise of smartphones, digital commerce has reached out to mobile apps. Companies make mobile versions of their online stores or devoted applications, making it much more helpful for clients to shop whenever, anyplace.
Electronic Payments: Digital commerce has popularized the utilization of electronic payment systems, including credit/debit card payments, online banking, and mobile wallets like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. These techniques take into account speedy, secure exchanges.
Digital Marketing and Advertising: Businesses utilize digital marketing techniques like search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, email marketing, and social media campaigns to attract and engage customers online, driving traffic to their e-commerce sites.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Digital commerce platforms utilize CRM systems to oversee associations with current and expected clients. This includes utilizing data analysis about clients’ history with the company to improve business relationships, focusing on customer retention, and ultimately driving sales growth.
Recommend Read: Enterprise Digital Transformation | The Future of Business Growth
E-commerce refers specifically to the buying and selling of goods and services over the Internet. It’s a subset of the more extensive idea of electronic business (e-business) and spotlights basically the transactional aspects of online retail. E-commerce incorporates activities like online shopping from websites or apps, electronic payments, and online auctions. The piece of digital commerce manages the trading of products and services for payment.
Digital Commerce, then again, is a more extensive term that extends beyond the transactional aspect of buying and selling online. It envelops the whole course of marketing, selling, servicing, and paying for products and services online.
This encompasses not only the direct act of selling and buying but also the activities that support these transactions, such as digital marketing, customer experience management, data analytics, and mobile commerce, including the development of user-friendly and engaging mobile apps.
Retail and eCommerce Mobile App Development has become an integral part of the digital commerce landscape, enabling businesses to connect with customers on their mobile devices, providing personalized shopping experiences, and facilitating seamless transactions. Digital commerce is more centered around the customer journey and experience in the digital environment, including how products and services are presented and how brands interact with their customers across various digital channels.
An example of digital commerce is the online retail giant Amazon. Amazon epitomizes digital commerce by offering a comprehensive online platform where customers can purchase a vast array of products ranging from books and electronics to groceries and clothing.
Beyond just a transactional website for purchasing goods, Amazon integrates various aspects of digital commerce: it provides personalized product recommendations based on user browsing and purchasing history, utilizes a sophisticated user review system to guide shoppers, offers various digital payment methods, and includes a robust customer service mechanism.
Additionally, Amazon’s mobile app allows for convenient shopping on the go, embodying the adaptability and customer-centric approach of digital commerce. This integration of diverse online shopping and service aspects makes Amazon a prime example of digital commerce in action.
Wider Customer Reach: Digital commerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing businesses to reach a global audience. This expanded reach means companies can attract customers from anywhere in the world, significantly increasing their potential market and customer base.
Convenience for Customers: Digital commerce offers unmatched convenience for shoppers. Customers can browse and purchase products or services at any time and from any location, as long as they have internet access. This 24/7 availability makes shopping easier and more accessible for people with busy schedules or those who live far from physical stores.
Lower Operational Costs: Operating an online store often requires lower overhead compared to traditional brick-and-mortar establishments. Expenses like rent, utilities, and in-person staff can be significantly reduced or eliminated. This cost-effectiveness can also translate into lower prices for consumers, making products more competitive.
Personalized Shopping Experience: Digital commerce platforms can collect and analyze customer data, such as browsing and purchase history. This data can be used to offer personalized recommendations, targeted promotions, and a tailored shopping experience, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Increased Sales and Marketing Opportunities: Digital commerce opens up an abundance of marketing opportunities open doors through digital channels. Businesses can engage in targeted advertising, content marketing, social media engagement, and email marketing to reach potential customers more effectively. Furthermore, the capacity to track and analyze customer interactions and preferences leads to more effective marketing strategies and, consequently, potentially higher sales.
Lack of Personal Touch: Digital commerce lacks the personal interaction that often comes with shopping in physical stores. Customers miss out on the experience of speaking with sales staff, getting immediate answers to questions, and the tactile experience of seeing and touching products before purchase.
Dependency on Internet Access and Technology: Digital commerce is entirely reliant on Internet connectivity and the availability of appropriate technology. This can be a significant barrier in areas with limited or unreliable internet access, and for individuals who are not comfortable with using digital technologies.
Security and Privacy Concerns: Online transactions carry the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks, which can compromise customer’s personal and financial information. Despite advancements in security technology, the fear of fraud and identity theft remains a concern for many consumers.
Delayed Gratification: Unlike shopping in physical stores where customers can immediately obtain their purchase, online shopping usually involves waiting for the product to be delivered. This delay can be a drawback, especially in situations where a product is needed urgently.
Difficulty in Assessing Product Quality: When shopping online, customers cannot physically inspect products before buying. This can lead to dissatisfaction if the product received does not meet expectations or differs from its online description or image. Additionally, the process of returning an unsatisfactory product can be inconvenient and time-consuming.
To wrap up, digital commerce has really changed how businesses work and how we all shop. We’ve taken a gander at what digital commerce is, the manner by which it works, and what it means for our lives and the world’s economy. It offers incredible things like making shopping simpler, reaching more customers, and giving people more personalized shopping experiences.
Be that as it may, there are a few disadvantages as well, similar to stresses over online safety and missing out on talking to people in stores. As innovation continues to improve and the manner in which we shop continues to change, digital commerce will turn out even more important in the way we trade things. Whether you’re at this point in business, considering beginning one or especially really like to shop online, it’s perfect to know how digital commerce works, especially as all that keeps on changing so rapidly.